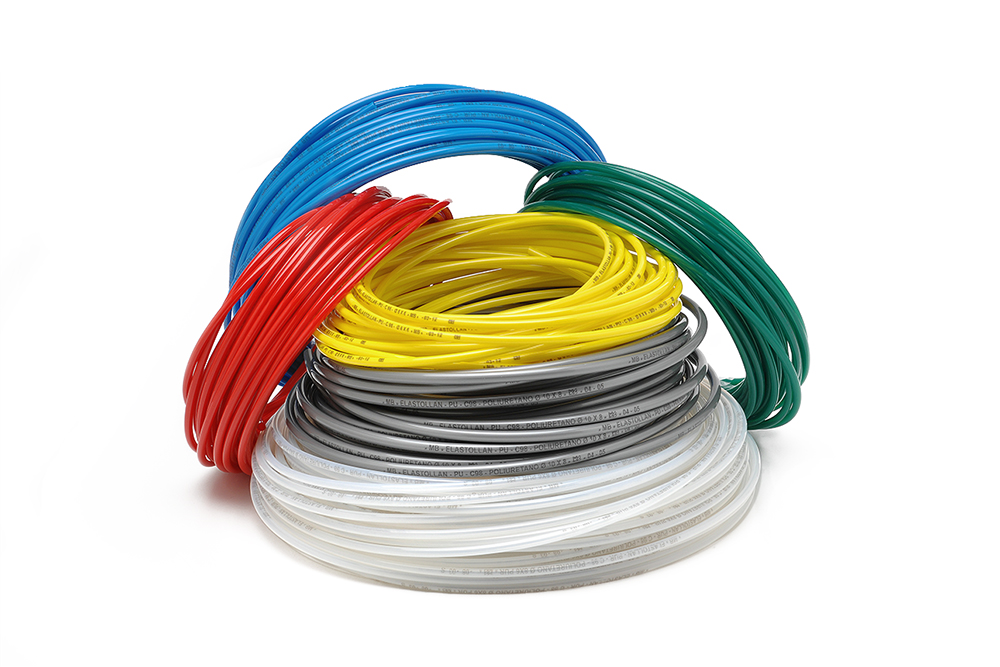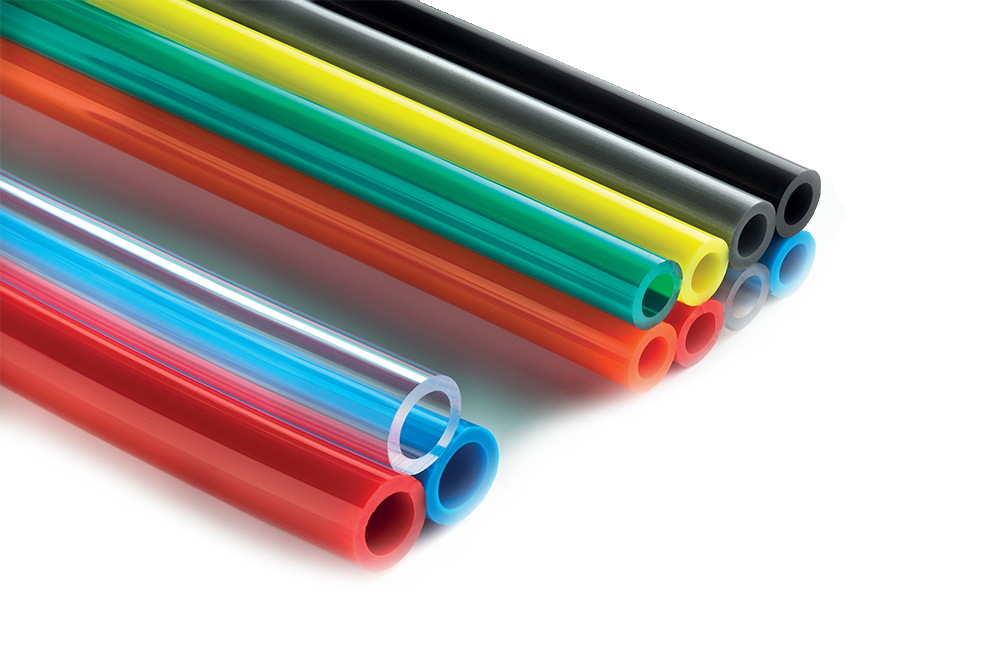

Ester polyurethane
Polyurethane exhibits a wide range of properties, due to the possibility to modulate the polyols, diisocyanates, catalysts, and additives. Ester-based polyurethane stands out for its optimal mechanical properties at room temperature as well as its resistance to ageing at high temperatures. It exhibits excellent resistance to abrasion and tearing. It is resistant to UV rays (if additives are used appropriately) and it has optimal barrier resistance to gases. Attention should be given to the chemical resistance of polyurethane, which in general is not high: once the polymer enters into contact with an aggressive substance, the degradative phenomena that are triggered lead to the rupture of the material; in most cases the structural failure of the tube is preceding by swelling. An example of these two phenomena is verified when the polyurethane is in contact with acids and concentrated alkaline solutions, which cause a rapid breakdown of its mechanical properties. Contact with saturated hydrocarbons, diesel gasoline, and kerosene (paraffin), instead, leads to swelling and a reduction in mechanics, but not irreversibly. This phenomenon is reversed once the solution has evaporated and the initial properties are restored. Polyurethane does not show problems when put into contact with oil lubricants and greases, but it does show sensitivity, in an irreversible way, to the additives contained in some lubrification products.
COMMON NAME
Polyurethane or Thermoplastic Polyurethane
MORPHOLOGY
Semi-crystalline or amorphous polymer
SYNTHESIS
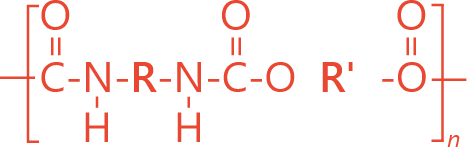
Ester polyurethane is formed from the polyaddition of ester-based polyols and diols in a chain. The chain length is variable and can be adjusted (with diisocyanates) to obtain different mechanical properties.
STRUCTURE
PROPERTIES
-
Dimensional stability
-
Excellent wear and abrasion resistance
-
Excellent resistance to traction and tearing
-
Excellent capacity for shock absorption
-
Optimal flexibility at low temperatures
-
Good impact resistance in the cold
-
Good resistance to high temperatures
-
Good resistance to oils, greases, oxygen, and ozone
-
Adjustable mechanical properties according to the application
-
Optimal colorability


