
LDPE
Low density polyethylene, LDPE, is a branched polymer characterized by the simultaneous presence of random short and long branches. The combination of these branches causes the density of the LDPE to vary from a minimum of 0.915 to a maximum of 0.935 g/cm3, where the range of densities between 0.926 and 0.935 is sometimes called “middle density M(L) DPE.” LDPE exhibits a good balance of mechanical, chemical, and aesthetic properties that are combined at a low cost. The manufacturing process is easy and optimal; the appearance of the surface, though, is accompanied by scarce resistance to scratching. LDPE has optimal properties at low temperatures but is not suitable for applications that demand elevated rigidity and traction resistance. It has optimal resistance to aqueous solvents, saline solutions, acids, alkanes, and alcohols, but it exhibits scarce resistance to oxidizing agents, aliphatic solvents, aromatic solvents, polar liquids, and chlorinated solvents.
COMMON NAME
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
MORPHOLOGY
Semi-crystalline Polymer
SYNTHESIS
Free radical polymerization of ethylene activated by peroxide catalysts and obtained at extremely high pressures (up to 2000atm) and high temperatures (200°C)
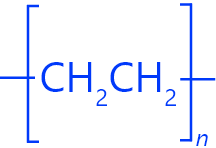
STRUCTURE
PROPERTIES
-
Dimensional stability
-
Resistance to hydrolysis
-
Low coefficient of friction
-
Excellent resistance to corrosion and chemicals
-
Low permeability to gases and vapors
-
Optimal flexibility at low temperatures
-
Excellent impact resistance at room temperature and cold temperatures
-
Lightness
-
Non-toxic
-
Odorless and tasteless